🤖 AI Expert Verdict
A data warehouse is a central repository used to store aggregated data from various operational systems. It processes and organizes data specifically to support analytics, business intelligence (BI) applications, and organizational decision-making.
- Provides faster access to data for quick business insights.
- Optimized for running complex analytical queries.
- Supports business intelligence (BI) and consistent reporting.
- Improves organizational strategic decision-making.
Data Warehouse: Complete Definition and Guide
A data warehouse (DW) is a central data repository. It collects data from operational systems and various other sources. This resource supports powerful analytics applications. These applications help drive crucial business decisions. Data warehousing is key to any robust data management strategy.
What is a Data Warehouse?
DWs process and organize stored data for analysis. Business analysts, executives, and data scientists use this information. Typically, a DW is a relational or columnar database. It lives in the cloud or an on-premises data center. Data comes from online transaction processing (OLTP) applications. It also comes from internal and external sources. The data is consolidated for business intelligence (BI). BI uses include querying, decision support, and reporting. Users access this data through BI software and analytics tools.
Understanding DW Architecture
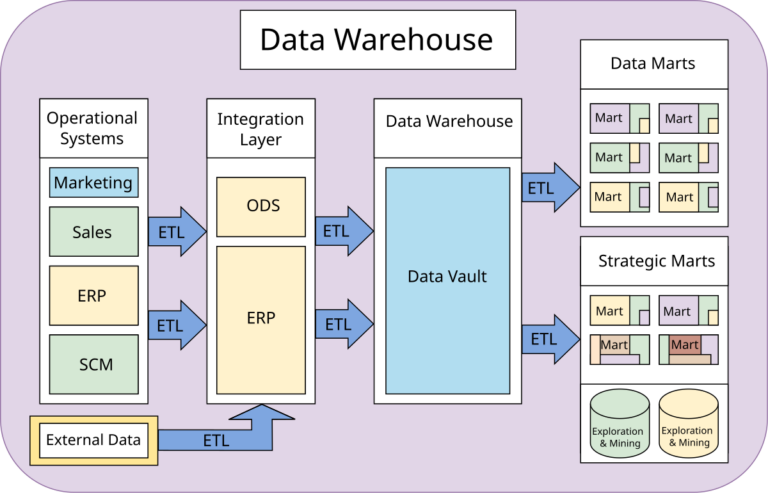
A fundamental DW architecture contains three tiers. It includes a data integration layer. Tools in this layer extract and combine data from operational systems. A staging area cleanses and transforms this data. It organizes the data before loading it into the warehouse. Data quality software handles tasks at this staging level. An enterprise data warehouse (EDW) stores analytical data for all operations. Alternatively, large companies may use separate data warehouses. DWs also connect to data marts. Data marts are smaller systems. They hold data subsets for specific users or departments.
Design Approaches: Inmon vs. Kimball
Organizations follow two main implementation paths. These are the top-down and bottom-up methods.
1. The Top-Down Method (Inmon)
William H. Inmon pioneered this approach. It calls for building the EDW first. You then use this centralized data to set up data marts. Data is validated in a staging area. It integrates into a normalized data model. This prepares it for planned BI and analytics uses.
2. The Bottom-Up Method (Kimball)
Ralph Kimball developed this alternative. This approach creates dimensional data marts first. Data models use a star schema design. Fact tables connect to one or more dimensional tables. Data marts can populate an EDW or integrate with each other. A hybrid approach combines aspects of both methods. Federated data warehouses integrate separate analytical systems.
Benefits of Data Warehousing
DWs offer business and IT advantages. They enable faster, more efficient data access. They have the compute resources for running complicated queries. Businesses derive quick insights and value from their data. Companies use DWs for enterprise reporting and strategic decision-making. Shop Our Products related to data solutions to maximize your efficiency.
[adrotate group=”1″]Data Warehouse Best Practices
Adopt these practices for better design and management.
Understand Business Goals
First, understand the goals driving the need for a DW. The DW holds structured data ready for analysis. IT leaders must involve business stakeholders. Their objectives shape decisions about data sources and formatting.
Review Data Governance and Security
Review your data governance program. Update your overall data management strategy as needed. Ensure source systems feed clean, accurate, and consistent data. Define user permissions and access controls upfront. Address broader data security and compliance requirements early.
Select the Right Architecture
Business requirements determine the best technology. Ask key questions: Do you need an on-premises or cloud DW? Should you use ETL or ELT methods? Will you deploy the platform yourself or use a managed service?
Optimize and Maximize Value
New practices help optimize management and value. Data observability maintains data health in pipelines. Applying Agile methodologies delivers value faster and lowers risk. Self-service BI capabilities also speed up value delivery. You can Read Our Blog for more insights on optimization!
Data Warehouse vs. Data Lake
Both systems support analytics, but they differ greatly. A DW stores processed, structured data. It uses predefined schemas for BI applications. A data lake is a repository for all types of raw data. This includes structured, unstructured, or semi-structured data. Data lakes commonly use big data platforms like Hadoop. They support advanced analytics like machine learning. DWs also differ from operational databases. An operational database collects data from a single system for ongoing processes. The DW consolidates and cleans this data for analysis.
A Brief History
IBM researchers Barry Devlin and Paul Murphy started the concept. They coined the term in their 1988 paper. Bill Inmon published his book in 1992, promoting the top-down design. Ralph Kimball introduced the bottom-up approach in 1996. Organizations widely adopted DW technology throughout the 2000s.
Reference: Inspired by content from https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatamanagement/definition/data-warehouse.