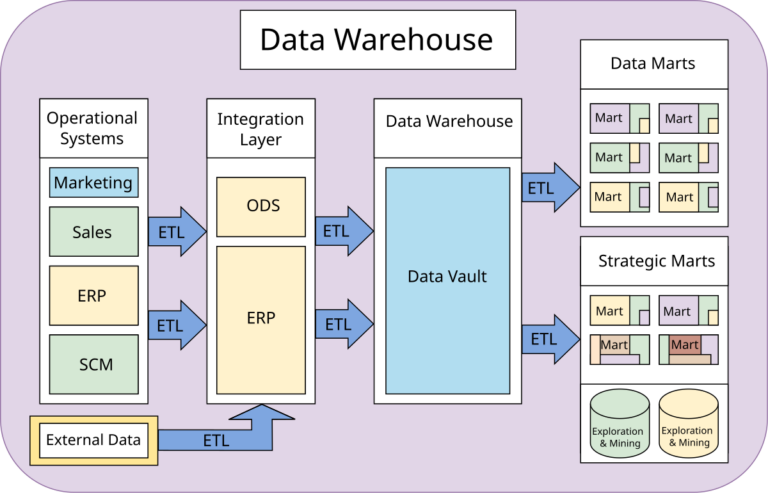
🤖 AI Expert Verdict
Data professionals today face an unprecedented challenge: organizations struggle with fragmented data ecosystems where AI initiatives demand contextually rich datasets that traditional pipelines often fail to deliver. You're not alone if you spend more time debugging integration failures than building innovative solutions that unlock business value from your data investments. The transformation of data engineering reflects broader shifts toward real-time decision-making and AI-driven operations. Modern enterprises generate massive volumes of information across cloud platforms, SaaS applications, and edge devices, creating integration complexities that legacy ETL systems cannot handle. Meanwhile, emerging requirements around data sovereignty, privacy compliance, and cost optimization demand architectural approaches that balance flexibility with governance. This comprehensive guide explores the evolving landscape of data engineering, from foundational concepts to cutting-edge practices like data mesh architectures and AI-augmented pipeline development. Whether you're transitioning into data engineering or advancing your existing career, you'll discover the skills, tools, and strategies needed to build resilient data infrastructures that power intelligent business applications.
- Enables AI innovation and model training with trusted data.
- Unifies fragmented data ecosystems into coherent models.
- Ensures regulatory compliance (GDPR, HIPAA) through governance.
- Accelerates time-to-insight from weeks to minutes.
- Improves data quality and accuracy using automated processes.
Data Engineering: Powering AI with Trusted Data
Data professionals face huge challenges today. Organizations struggle with fragmented data ecosystems. Traditional pipelines often fail to deliver rich datasets for AI initiatives. You likely spend too much time debugging systems. Instead, you need time to build innovative solutions.
Data engineering is changing rapidly. It shifts toward real-time decisions and AI-driven operations. Modern businesses create massive data volumes. This data lives across cloud platforms, apps, and edge devices. Legacy ETL systems cannot handle these integration complexities. New demands for compliance and cost optimization also arise. This guide explores the evolving world of data engineering.
What is Modern Data Engineering?
Data engineering builds and manages infrastructure. This infrastructure collects, transforms, and delivers data at scale. It forms the foundation for data science and analysis. It allows teams to access reliable, high-quality information.
Modern data engineering goes beyond traditional ETL. It now includes real-time streaming and automated governance. Data engineers architect these systems. They handle structured and unstructured data from diverse sources. They ensure information flows seamlessly to analytical platforms. They maintain strict security, compliance, and performance standards.
This discipline evolved with cloud computing and AI. Data engineers now work with distributed systems. They use microservices and intelligent automation. This requires expertise in cloud-native tools. These tools support elastic scaling and real-time processing.
Why Does Data Engineering Matter?
Data engineering turns raw data into actionable insights. It creates reliable pipelines. These systems deliver consistent, accurate data to business stakeholders. Well-engineered systems reduce insight delivery time from weeks to minutes. Organizations can then respond quickly to market changes.
Unifying Fragmented Data Sources
Modern enterprises use many applications. They use dozens of SaaS apps and cloud services. Data engineering unifies these sources. It creates coherent data models. This provides comprehensive views of business operations.
Improving Data Quality and Accuracy
Validation, cleansing, and standardization automate this process. Data engineering removes inconsistencies. It fills missing values and improves data accuracy. This quality assurance prevents costly decisions based on bad data. It lets AI systems operate on trusted datasets.
Democratizing Access
Good infrastructure allows teams to access data independently. They use self-service platforms. This reduces reliance on technical teams for routine analysis. It accelerates insight generation. It frees engineers to focus on platform optimization.
Ensuring Governance and Compliance
Data engineering implements security controls and encryption. It establishes access governance. This protects sensitive information. It meets rules like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. These safeguards are vital as data volumes increase.
Powering AI and Machine Learning
Machine learning models need high-quality training data. Data engineering creates the stable, scalable infrastructure. This supports AI applications like recommendation engines. It ensures data freshness for optimal model performance.
The Role of a Data Engineer
A data engineer is a specialized IT professional. They build and maintain the infrastructure. This infrastructure enables organizations to process and analyze data at scale. They bridge software engineering and data science. Data engineers focus on the technical systems that drive analytics.
Essential Skills and Technologies
Programming Languages
Python remains dominant for data engineering. It offers libraries for pipeline orchestration. Java and Scala provide better performance for large processing jobs. This is useful with Apache Spark and Kafka. Mastery of SQL is also essential. It goes beyond basic queries to include complex optimization.
Database Expertise
Data engineers must understand relational databases. They must also know NoSQL systems. They choose the right technology for performance and cost efficiency.
Cloud Platforms and Infrastructure
Expertise in AWS, GCP, and Azure is required. Knowledge of managed data services is critical. Familiarity with serverless computing and Kubernetes is valuable. Tools like Terraform enable reproducible deployments.
If you are ready to implement new data solutions, you can always Shop Our Products.
[adrotate group=”1″]Streaming and Real-Time Processing
Apache Kafka dominates event streaming architectures. Apache Flink handles sophisticated stream processing. Understanding event-driven architectures is key. This is essential for building responsive systems.
Modern ELT and Data Transformation
The shift to ELT leverages cloud data warehouses. Tools like Airbyte offer hundreds of pre-built connectors. dbt enables analytics engineering. It uses SQL-based transformations and version control.
Data Reliability (Observability)
You must understand the five pillars of observability. These are freshness, quality, volume, schema, and lineage. This enables proactive data reliability management. Tools provide automated anomaly detection.
AI Integration Components
Supporting AI needs knowledge of vector databases and feature stores. Data engineers must manage model training datasets. They must support real-time inference. They must also maintain governance standards.
Key Practices in Modern Data Engineering
Adopting Lakehouse Architectures
Create cloud-native infrastructure. Lakehouse patterns combine data lake flexibility with warehouse performance. This involves selecting formats like Delta Lake or Apache Iceberg. You implement separation of storage and compute. These systems support both batch and streaming workloads.
Building Automated Pipelines
Build automated workflows using ELT patterns. Implement Change Data Capture for real-time sync. Create self-healing pipelines with intelligent error handling. Establish monitoring systems using AI for anomaly detection.
Implementing Data Observability
Implement comprehensive observability frameworks. Monitor data across five dimensions. Create automated validation rules. Establish data contracts between systems. These quality metrics provide early warnings of issues.
Designing Data Mesh Architectures
Design domain-oriented data architectures. Business teams own their data products. You maintain centralized governance standards. Self-serve platforms enable domain autonomy. They enforce global policies for security.
Supporting AI Workflows
Build infrastructure for machine learning. This includes feature stores and vector databases. Ensure pipelines deliver high-quality datasets. This is required for accurate AI model performance.
The Future: Data Contracts
Data contracts represent a major shift in managing quality. They establish formal agreements. These agreements exist between data producers and consumers. Contracts specify structure, quality metrics, and SLAs. This ensures reliable information for all systems. To learn more advanced topics, be sure to Read Our Blog.
Reference: Inspired by content from https://airbyte.com/data-engineering-resources/data-engineering.