🤖 AI Expert Verdict
A data warehouse is a centralized repository that stores structured and semi-structured data for analysis and reporting purposes. It consolidates data from multiple sources, cleans and standardizes the information, and provides fast access to long-term historical data, enabling organizations to make more informed business decisions through tools like data mining and visualization.
- Consolidates data from disparate sources into a single source of truth.
- Provides reliable, vetted, and consistent historical data for long-term analysis.
- Greatly reduces query times, improving analytics performance.
- Optimized for structured data and predefined business intelligence (BI) use cases.
What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse (DW) is a central storage hub. It keeps structured and semi-structured data. This includes database tables, Excel sheets, and XML files. Organizations use this data for analysis and reporting. Data comes from many sources. These sources include point-of-sale systems and business applications. The data is cleaned before it enters the warehouse. A DW stores huge amounts of historical data. Users easily access this information. They use it for data mining and visualization. Reliable data helps users make smarter decisions. Data warehouses make this possible.Key Benefits of Data Warehousing
Enterprise data warehousing offers many benefits. Key advantages include:- You consolidate data from multiple sources. This creates a single source of truth.
- You can analyze long-term historical data.
- The DW cleans and standardizes data. This makes information accurate and consistent.
- It greatly reduces query times. This boosts overall system performance.
- You load data efficiently without deployment costs.
- The system secures and protects your private data.
- You prepare data for advanced analytics like visualization.
Data Warehouse vs. Data Lake: Key Differences
What separates a DW from a data lake? Both are repositories. They both store and process data. However, they serve different use cases. Many organizations use both systems together. A DW is relational. The data structure is predefined. This schema is optimized for SQL queries. You use data warehouses for specific purposes. This includes BI analysis or identified business use cases.Data lakes handle structured and semi-structured data. They also accept raw, unprocessed data. This comes from sources like IoT devices or social media. They use a “schema on read” approach. The structure is defined when you read the data. Data lakes are flexible and scalable. Data scientists use them for machine learning.
| Feature | Data Lake | Data Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Structured, semi-structured, unstructured | Structured |
| Schema | Schema on read | Schema on write |
| Data State | Raw, unfiltered | Processed, vetted |
| Typical Users | Data scientists, data engineers | Business analysts |
[adrotate group=”1″]
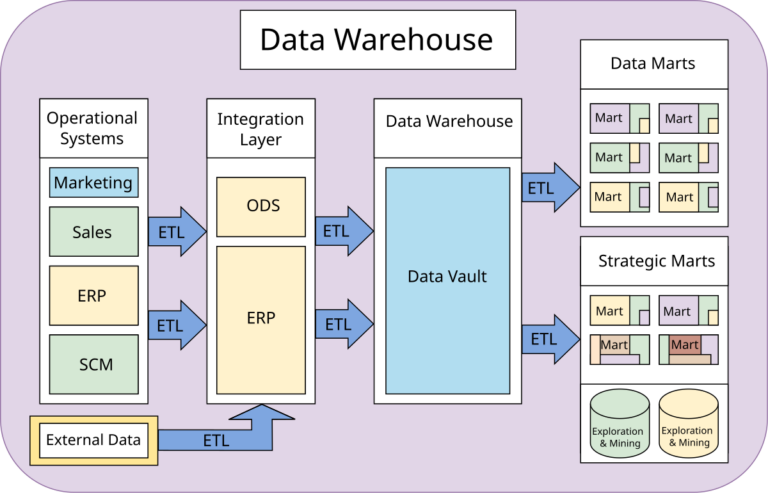
How a Data Warehouse Works: Design and Tiers
A DW is a complex, structured system. It uses multiple interacting tiers. This design handles your data effectively.1. The Bottom Tier (ETL and Storage):
Data moves from sources into this tier. It is cleaned and transformed. This is the Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) process. This tier stores and optimizes data. This optimization leads to faster query times.
2. The Middle Tier (Analysis):
Here you find the analytics engine. It is also called the OLAP server. OLAP servers access massive data volumes quickly. This provides lightning-fast results.
3. The Top Tier (Presentation):
The front-end interface lives here. It visually presents the processed data. Analysts use this for reporting and self-service BI needs.
Essential Data Warehouse Tools and Components
Consider your long-term goals when designing a DW. Think about your data’s nature. How many sources will you integrate? Will you automate your workflows? Your specific needs determine the complexity. A typical enterprise DW needs several components. Many companies offer data warehouse software. You need the right tools for a cohesive solution. Essential products include:- Cloud-Based Solutions: Unified, cloud DW solutions offer scaling ability. They lower costs and increase speed. (e.g., Azure Synapse Analytics).
- ETL Pipelines: These tools automate workflow creation and scheduling. They integrate and standardize source data automatically.
- Object Storage: This holds large amounts of structured and unstructured data. It stages source data before loading it into the warehouse.
- Distributed Storage: This uses relational tables with columnar storage. It improves query performance and reduces costs.
- Resource Manager: This allocates computing power to your workloads.
- Business Analytics Tools: These deliver insights via dashboards and reports.
- Security Features: Data encryption and user authentication protect your assets.
A data warehouse is vital for business intelligence. It provides reliable, centralized data. This allows organizations to move forward confidently. The capabilities of Azure SQL Data Warehouse now belong to Azure Synapse Analytics. Customers use the dedicated SQL pool feature. They manage their existing warehouse data easily. They gain advanced analytics features. This includes serverless data lake exploration.
Reference: Inspired by content from https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/resources/cloud-computing-dictionary/what-is-a-data-warehouse/.